Radicular cyst - Differential diagnosis
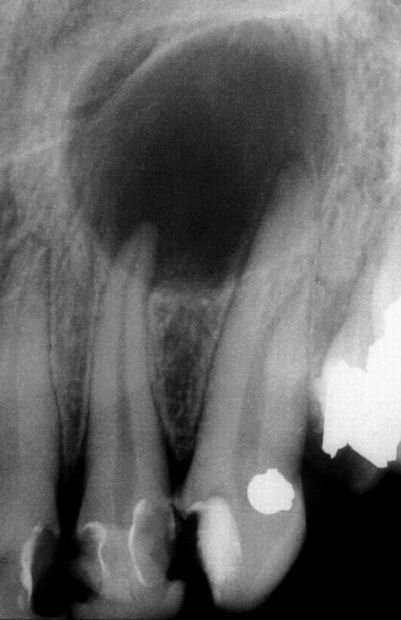
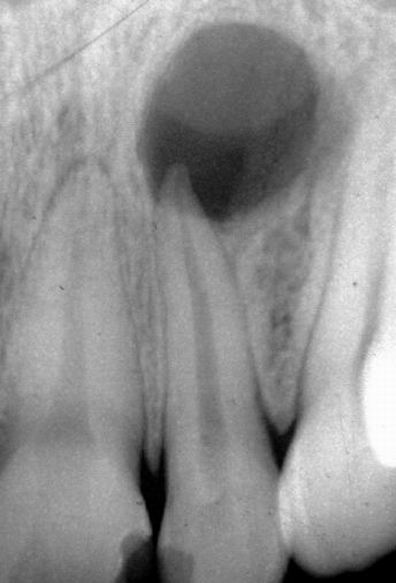


Differential diagnosis between a radicular cyst and apical periodontitis cannot be reliably made without a histological examination of periradicular tissues. The pulp is necrotic in both and can be either symptom-free or symptomatic.
Differential diagnosis between a radicular cyst and other jaw cysts also requires a histological analysis. However, while the tooth is always necrotic in a radicular cyst, it is usually vital with other cysts, unless necrosis has been caused by other factors. Radiographic diagnosis of a traumatic bone cyst is particularly important because usually no treatment is required.
Although the tooth is vital in many cysts, preoperative endodontics may be needed, if surgical excision of a large cyst (such as keratocyst or nasopalatine cyst) is likely to damage nerves and blood vessels of the tooth/teeth next to the cyst. Consultation with a radiologist / oral surgeon is recommended with all larger suspect lesions.