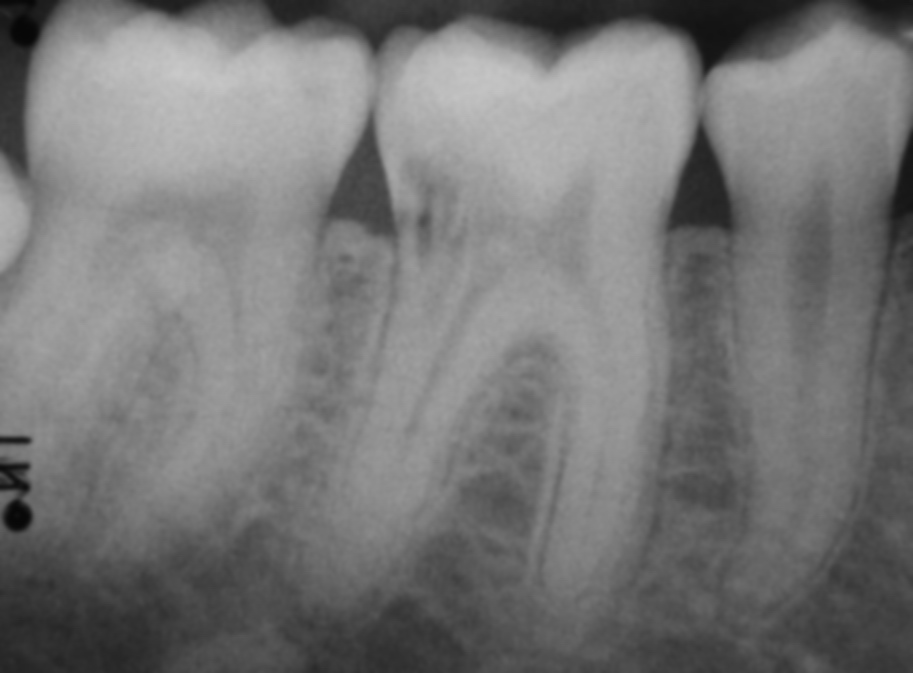
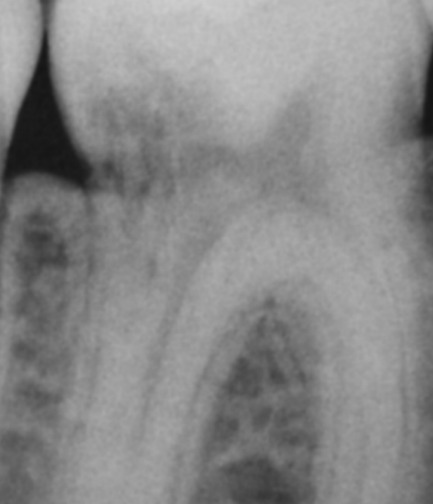


Areas with reduced radiolucency were detected in lower right first molar of a young patient in a routine radiographic investigation. The appearance was untypical of a carious lesion, therefore it was decided to obtain a CT scan of the tooth to verify a tentative diagnosis of cervical root resorption, and to evaluate the size of hard tissue destruction and the bucco-lingual location of the obvious perforation.