Table 1
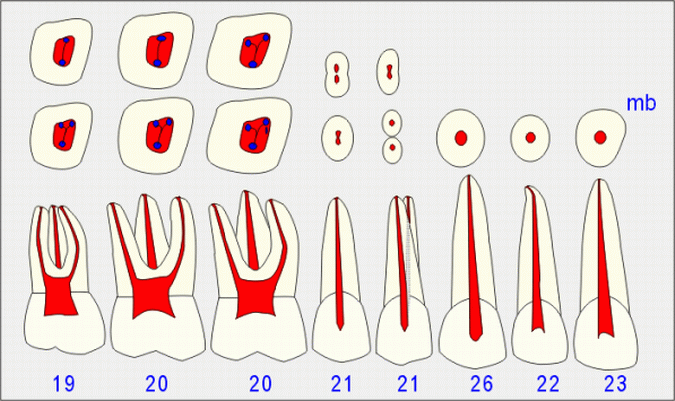

The average length of teeth in the upper jaw varies from 19mm to 26 mm. The canine is the longest tooth in the upper jaw followed by the central incisor.
The central incisor is the only tooth that is regularly straight to the root tip. The lateral incisor typically has a distal or buccal apical curvature. Upper canines may be straight but may also curve buccally or distally. Most teeth in the premolar and molar regions have curved roots.
Double canals are practically never found in upper incisors or canines. Single-rooted premolars and mesiobuccal roots of upper molars often have double canals. As in the lower jaw, double canals are located in the bucco-lingual dimension.